Brain Tumor
A brain tumor is a mass of abnormal cells that grows in the brain. Brain tumors can be benign or malignant. Benign tumors are noncancerous and grow slowly in some years. Malignant tumors are cancerous and and grow rapidly in months. Brain tumor surgery is a complex procedure that involves the removal of a tumor from the brain while preserving the normal parts of brain. It is a major operation, but it can be a life-saving treatment for people with brain tumors.
The symptoms of a brain tumor
Headaches are the most common symptom of a brain tumor. They can be severe and persistent, and they may be worse in the morning or when you lie down.
Seizures are sudden bursts of electrical activity in the brain. They can cause a variety of symptoms, including sudden jerky muscle contractions, loss of consciousness, and changes in behaviour.
Brain tumors can affect vision in several ways. They can cause double vision, blurred vision, or loss of vision in one or both eyes.
Brain tumors can affect the nerves that control body movements and sensations.
This can cause weakness or numbness in the arms or legs on one side of the body.
Brain tumors can affect the areas of the brain that are responsible for speech and language. This can cause difficulty speaking, understanding speech, or finding words.
Who needs brain tumor surgery?
Surgery is the primary modality of treatment for brain tumors. The surgery is done to
1) remove the entire tumor and
2) send the tumor for laboratory analysis.
All patients diagnosed with brain tumours need surgery. However, some benign tutors which are small in size (<2cm) can be treated by radiosurgery (Cyberknife).
How is brain tumor operation performed?
Brain tumor operation is typically performed by a neurosurgeon, who is a doctor who specializes in surgery of the brain and spinal cord. The type of surgery used will depend on the size and location of the tumor. The most common type of brain tumor surgery is “Microscopic Tumor Removal Surgery”.
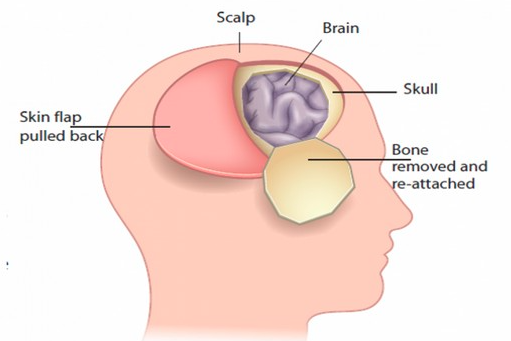
In this surgery, the surgeon makes an incision in the scalp and removes a piece of bone from the skull to access the brain. The surgeon then removes the tumor under operating microscope, fixes the skull bone back in place and closes the incision.
In some cases, brain tumor surgery may be performed using minimally invasive techniques, such as endoscopic surgery. In endoscopic surgery, the surgeon uses a thin, tube-like instrument with a camera and light at the end to access the brain. The surgeon then removes the tumor using small instruments inserted through the tube.
Does my normal brain areas get damaged during brain tumor surgery?
No. The normal brain areas are identified separately from tumor via various methods. The operating microscope offers magnification upto 10x and helps separating normal brain areas. Some types of dyes are used during surgery, such as ALA dye, which stains only the tumor. In addition, ultrasonography is used during the surgery, to separately identify tumor and normal brain. These steps help preserve the normal brain during tumor removal surgery.
What is the recovery process like after brain tumor surgery?
The recovery process after brain tumor surgery can vary depending on the type of surgery performed and the patient’s overall health.
Typically, the patients are observed in Neurocritical care unit for 24 hours. They are made to stand and walk 24 hours after there surgery. They are shifted to normal wards/rooms for 2-3 days, during which they undergo physical therapy which helps them regain their strength and function.
Conclusion
Brain tumor surgery is a complex procedure but safe procedure. It can be a life-saving treatment for people with brain tumors. If you are considering brain tumor surgery, it is important to talk to your doctor to discuss the benefits and risks of the procedure. You should also ask about the recovery process and what you can expect after surgery.


Leave a Reply